Challenge
In the project, five organisations from four countries (Germany, Scotland, Spain and Austria) are working on supporting accompanying and transition processes with the help of digital technologies. Each of these organisations has, e.g., its own established processes, specifics regarding their target group, employees and framework conditions, administrative responsibilities, legal claims and the terminology used also differ considerably.
One of the first questions in the project context was therefore how we can avoid these differences hindering us in finding solutions that fit for everyone.
Solution
As a possible solution, those involved in the project have placed the focus on what they have in common, since – despite all their differences – they are united by a shared goal.
Approach
Interviews were conducted with participants from the five organisations in order to better understand the respective procedures and specific process steps as well as the quality goals pursued within the framework of transfer processes. Based on these results, procedures that could be found in a similar way in all organisations were combined into unified process steps.
Result
The result is a uniform process model whose phases can be found everywhere (even if under different names), and which are also filled with life in different ways. In this way, the model also provides a standardisation of the language used within the project.
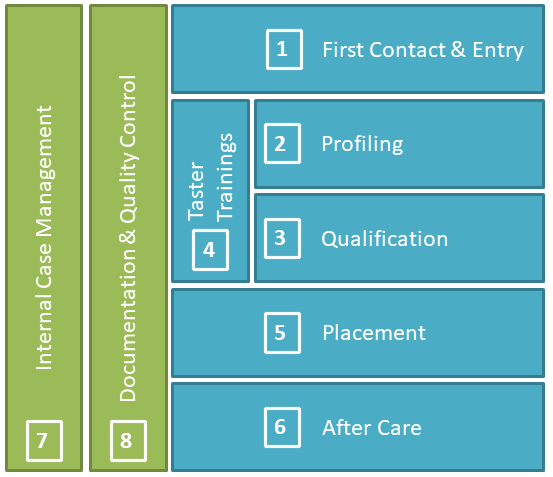
Click the phase number below to see more detailed information on what this particular phase may cointain.
Phase 1: First Contact & Entry
This phase may contain:
- First contact
- Basic information / consultation (often 1:1)
- Clarification of funding
- Documentation of the person‘s case history
- Identification of interests and partly already of skills
- Assignment to preliminary support team (participant, jobcoach, trainer)
- Decision and agreement on entry date
Phase 2: Profiling
This phase may contain:
- Identification of
- strengths & weaknesses
- support needs
- family context
- potential
- Approaches
- Try out & exploration
- Creation of vocational profiles by specialised staff
- Stress testing (formalised procedures)
- Networking with third parties
- circle of supporters
- medical doctors
- counselling services etc.
- Matching between clients and job coaches
- Final feedback talk with participant
- Verification of previous assumptions at later stages (as profiling never ends)
Phase 3: Qualification
This phase may contain:
- Trainers in lead
- Linking the different aspects from profiling
- Agreement on objectives
- Trainings on, e.g.,
- hygiene, healthy food
- general skills, social skills, managing emotions, confidence, changing role as adults
- Working with computers / ECDL, PC training, office service
- CV and interview training
- Modalities
- internal
- external (e.g. in cooperation with other partners, vocational school)
- Approaches
- Seminars and conversations
- Group talks, peer learning
- Fully structured timetable with individualised module selection
- Definition of thematic foci in a pre-defined cycle
- Repetitions always possible
- Even during external internships, participation in qualification modules, follow-up trainings or projects
- Job coach already in touch with participants
- This phase may last for many years
Phase 4: Taster Trainings
This phase may contain:
- Work placements for diagnostic assessment or to align expectations / wishes with reality
- short & sharp, sometimes just 1-day internships, small tasters
- Sometimes these placements lead to a job, but no expectations
- Modalities
- Externally: E.g., longlasting co-operation with selected companies that are well-sensitised regarding the target group
- Internally: E.g., internship(s) at own restaurant, gardening service, office service, or writing and painting workshop
- Participants most of the time in internships
Phase 5: Placement
This phase may contain:
- Job coach in lead
- Often 1:1 with employment coordinator / job coach
- Exploring different vacancies
- Contact with employers
- Job applications (also in earlier phases)
- Placement as an intern with the aim to evolve to an employee with contract
- 1-day work trials instead of interviews if appropriate
- Conclusion of a contract
- Networking and adaptation of external conditions; sometimes with
- friends & family
- round tables
- school social work
- vocational teachers
- Training in company
- Job coach supports daily at the workplace
- Job coach sometimes acting as a job assistant as well (very practical support during the first days)
Phase 6: After Care
This phase may contain:
- First place, then train (supported employment approach, seamless transition from placement to after care)
- Activity
- Depending on the level of required support, the job coach continues to visit at the workplace
- Support at the workplace requested by almost everybody
- Induction support
- Duration
- Up to 3 months aftercare (longer if needed, e.g., in crisis situations)
- At least 6 months after care
- Up to 1 year, might be extented (maximum 3 years in total)
- Focus
- Focus on participant, but often a more general role as a mediator is required
- Exchange with employer / direct superior
- Finding somebody in the company to work as a workplace buddy / mentor
- Discreet support if requested by participant, then working in the background
- Link to own organisation
- Staying in touch even with participants with a high level of autonomy who do not visit the organisation anymore
- Participation once per week in a group meeting in the organisation, where participants discuss and try to solve their current problems (job coach only moderates discussions)
- Once per month meeting with a second JC to discuss problems, including those with the first JC
- Handover to a different service, for long-time support
Phase 7: Internal Case Management
This phase may contain:
- One person centrally overseeing all cases
- Person-centred planning done by one person centrally
- Senior managers overseeing the activities of frontline staff
- Sub-sets of colleagues are forming teams
- Staff meets regularly
- Interviews with families are performed by two staff members
- Termination
- Missing willingness to work or quitting to attend interviews: exit of participation, but trying to link clients back where they came from
Phase 8: Documentation & Quality Control
This phase may contain:
- Lots of documentation
- Using forms (both internally developed as well as externally prescribed)
- Clear process instructions for participation and premature termination of participation
- Periodic financial compliance checks
- Use of a document server / database / customer relationship management software
- Time spent with clients
- Activities
- Phone talks
- Meetings
- Agreements (e.g. of target agreement talks)
- Resuts of any kind of assessments (e.g., Performance and Behavioural Appraisal – PBA)
- Reports sent to externals
- Quantitative indicators: e.g., number of contracts, hours spent per week per client, contribution to the quality of life
- Comments
- Periodic internal audits (e.g. random documents are looked up, practice situations are reflected)
- Training of all staff
- Patron system
- ISO certification